- Software
- Blockchain
- Web3 product
- Smart Contracts
- Mobile app
- Web platform
- AWS Cloud
- NFT marketplace
- DeFi
- Fintech
- AI product
- dApp
- Crypto wallet
Rumble Fish helps entrepreneurs build and launch bespoke digital products.
We take care of the technology, so you can focus on your business
Join the ecosystem
of our satisfied customers:









of our satisfied customers:










Who we are?
Hi there! We're Rumble Fish - a team of world-class experts in bespoke software development. Our engineers are highly skilled in blockchain, cloud solutions, and defi/fintech development. Our strength and pride is the ability to take ownership of the entire development process and be a true partner and advisor for our customers. Our mission is to craft state-of-the-art digital products using battle-tested technologies. Try us!
40uniquely skilled devs
1pet-friendly office
8years in business
42projects
999passion for coding
What do we do?
Software Development Services and Skills for your needs
Our team is well-versed and experienced in various blockchain development tools and technologies. Our unique skillset allows us to be at the forefront of Web3 development services so if you’re looking for a trusted IT partner to boost your decentralized product - look no further!
We deliver production-ready zero-knowledge proof solutions that actually ship to mainnet, specializing in custom ZK development, rollup scaling solutions, and privacy-preserving smart contracts that reduce processing times from hours to minutes. Try us!
We build fast, compliant, and cost-effective blockchain solutions on the XRP Ledger. From payment systems and tokenization platforms to enterprise DeFi applications, our team delivers production-ready systems that work when billions are on the line.
We build smart contracts that handle real business complexity without the usual blockchain headaches. From DeFi protocols to custom on-chain systems, we deliver production-ready solutions that scale.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) development requires an extensive amount of blockchain knowledge, as well as a great understanding of financial mechanisms. We’ve got both that bases covered! Our team has successfully built an impressive number of DeFi products like cryptocurrency exchanges, dApps, lending protocols, or staking platforms. Try us!
Our experienced team will take your AWS cloud solutions to the next level. AWS provides purpose-built tools to support your needs, and it is the preferred choice for any blockchain project. From the plethora of cloud tools and solutions offered by Amazon Web Services, we’ll help you choose and implement the ones that serve your business the best way possible.
AI chatbots can bring value to a wide range of industries by enhancing customer interactions, streamlining processes, and improving overall efficiency. We'll craft a perfect AI assistant for your product.
Need realistic data for AI training, testing, or product development—but privacy, scale, or availability is blocking you? We engineer custom synthetic data solutions that capture the complexity of real-world data without the constraints. From multi-modal generation to domain-specific datasets, we build what platforms can't deliver.
We build custom AI knowledge management systems that turn your scattered enterprise knowledge into instant, accurate answers - no more employees wasting their valuable time hunting through SharePoint and Slack for information. Unlike platforms that trap you in subscriptions, we engineer RAG solutions specifically for your data and security requirements, then hand you complete ownership of the source code and infrastructure.
Looking for a skilled team to help you build an advanced fintech platform able to compete with the biggest in the game? At Rumble Fish, we’ve got what it takes to engineer innovative financial technology systems. We offer end-to-end fintech software development, consulting, and expertise.
Our experts provide you with knowledge, skills, and experience that elevates every project to another level. We’ll gladly take ownership of the entire process and guide you and your team through the intricacies of cutting-edge technology development.
If you’re in need of professional web development services, look no further! Rumble Fish's talented team has extensive experience in delivering top-tier web apps and websites with the use of battle-tested tools and technologies like React or Nest. We know just the right solutions to exceed your business requirements.
Whether you need an Android, an IOS app, or both, the Rumble Fish team is here to help you deliver the beautiful and efficient mobile product that your customers will simply love to use! We craft fast and secure mobile apps with a wow factor to help our customers grow their businesses and reach their goals quicker.
If you're looking for a team capable of turning your product concept into a beautiful and technologically intricate digital solution - look no further! Rumble Fish is your trusted software development partner ready to take you through the entire process of custom digital product creation - from the early stages of ideation to the post-launch support. Whether you're on a mission to build a mobile app, a Web3 product, or an advanced platform - we are here for you!
We design sleek, intuitive, and highly effective interfaces to help you overcome your business challenges. After carefully evaluating and understanding your requirements we switch to the designing mode - the end goal is the beautiful digital solution that people love to use!
Testimonials
See what our customers say about working with us“
Latest case studyBridging Tari to Ethereum: WXTM & Secure Tokenization
Bridging Tari to Ethereum: WXTM & Secure Tokenization
Tari is an innovative L1 protocol focused on digital assets and privacy-preserving smart contracts. As a relatively new blockchain entering the crypto landscape, Tari faced a critical challenge: how to integrate their native XTM tokens with the broader DeFi ecosystem to enable trading, liquidity provision, and participation in decentralized finance protocols.
Collaboration timeframe:2 months
Services:Smart Contract Development, Blockchain Development, DevOps, Front-End Development, Back-End Development, AWS Cloud Solutions
We're trusted by global innovators and leaders.Join them!
TURNTABLE
A hybrid of a social network and a music appTURNTABLE
MAKERDAO
The first truly decentralized stablecoin crypto on EthereumMAKERDAO
ZBAY
A private inbox, wallet, and marketplace all in oneZBAY
VERIFYID
An identity verification MVPVERIFYID
Rumblefish Blog Synthetic Data Generation: A Complete Guide for 2026If you're building AI models, running software tests, or navigating the maze of data privacy compliance, you've probably run into the same wall: the data you need is either locked away, too expensive to collect, or legally off-limits. Synthetic data generation is how the smartest teams are breaking through that wall - and in this guide, we'll show you exactly how it works.
Synthetic data generation is the process of creating artificial datasets that replicate the statistical properties, patterns, and correlations of real-world data without incorporating any actual individual records or sensitive information. This technology has become essential for organisations navigating the intersection of data-driven innovation and privacy compliance. At Rumble Fish, we've seen this challenge play out across DeFi protocols, fintech platforms, and AI-powered products. Whether you're simulating on-chain transaction behaviour, generating training data for ML models, or stress-testing a financial system, synthetic data is no longer a workaround - it's a battle-tested strategy.
---
**TL;DR**
Synthetic data generation uses algorithms, statistical models, and AI techniques to create artificial data that preserves the statistical properties of real data while eliminating privacy risks. The generation process analyses original data patterns and recreates them as entirely new data points that contain no traceable personal information.
---
After reading this guide, you will understand:
* How synthetic data generation processes work at a technical level
* The different types of synthetic data and their specific applications
* Which tools and frameworks fit your use case
* How to address data quality, scalability, and compliance challenges
* Practical steps to implement synthetic data in your development workflow
* Why custom engineering often beats off-the-shelf platforms - and when to use each
## Understanding Synthetic Data Generation
Synthetic data generation refers to **creating artificial data that maintains the utility and statistical characteristics of existing data** without exposing sensitive production data. This artificially generated data serves as a privacy-preserving alternative for AI training, test data generation, analytics, and simulations across industries. For modern software development teams, the ability to generate synthetic data solves several critical problems: data scarcity in underrepresented scenarios, privacy restrictions on production data access, and the high costs of acquiring and labelling real data. Data scientists can train robust machine learning models, run load and performance tests, and develop new features without ever touching actual sensitive information.
### Types of Synthetic Data
**Structured synthetic data** includes tabular data, relational database records, and financial transaction logs. This type is particularly valuable for fintech applications where generating realistic tabular data enables fraud detection model training and payment system testing without exposing real customer data to risk.
**Unstructured data** encompasses images, text, audio, and video generated through deep learning models. Natural language processing applications benefit from synthetic text that mimics real communication patterns, while computer vision systems train on generated images representing scenarios difficult to capture in production.
**Time-series synthetic data** covers sensor readings, transaction logs, market data, and sequential events. For blockchain and DeFi applications, this includes simulated on-chain activity, protocol interactions, and smart contract transaction patterns that would be impossible to collect at scale from live networks.
Each type connects to specific development needs: structured formats support database testing and analytics, unstructured formats enable AI model training, and time-series data powers simulation and performance testing.
### Synthetic vs. Real vs. Anonymised Data
Traditional anonymisation techniques - data masking, tokenisation, generalisation - modify real data to obscure identities. However, these approaches carry re-identification risks when combined with external datasets, and often degrade data utility by removing the contextual information essential for analysis. Synthetic data fundamentally differs because **it contains no actual data from real individuals**. The generator creates data that is statistically identical to the source but shares zero one-to-one correspondence with original records. This distinction matters significantly for regulatory compliance: while anonymised data may still fall under GDPR or HIPAA scope if re-identification is possible, properly generated synthetic data typically does not. The utility preservation advantage is equally important. Anonymisation often destroys the correlations and statistical relationships needed for meaningful analysis. **Synthetic data maintains these patterns - mean, variance, multivariate dependencies - while eliminating privacy risks entirely.**
## How Synthetic Data Generation Works
The synthetic data generation workflow follows a consistent arc: analyse source data to extract patterns, build models that capture those patterns, and generate new data points that embody the learned characteristics without reproducing original records. The sophistication of each step determines the quality and utility of the resulting synthetic datasets.
### Statistical Distribution Modelling
Statistical approaches form the foundation of many synthetic data generation pipelines. The process begins with analysing the probability distributions present in the original data - identifying whether variables follow Gaussian, uniform, exponential, or custom distributions, and estimating their parameters.
Copula models extend this by capturing multivariate dependencies between variables. Rather than assuming independence or simple correlations, copulas model the joint distribution structure, enabling the generation of data samples that honour complex relationships between columns in tabular data - critical when, for example, a synthetic financial transaction needs to respect correlations between amount, merchant category, and time of day. These methods excel when interpretability matters and when data relationships are well-understood. Implementation complexity varies: univariate distribution matching is straightforward, while accurately modelling high-dimensional dependencies requires careful statistical validation.
### Machine Learning-Based Generation
Machine learning models learn patterns from training data through supervised and unsupervised approaches. Neural networks, particularly deep learning models, capture non-linear relationships and complex feature interactions that statistical methods can miss. Supervised approaches train on labelled datasets to generate synthetic data with known properties. Unsupervised methods discover latent structure in unlabelled data, enabling the generation of realistic data that reflects inherent patterns without explicit specification. **The relationship between ML and statistical methods is complementary:** statistical techniques provide interpretable baselines and work well for structured formats, while ML approaches handle the complexity of unstructured data and high-dimensional feature spaces where explicit modelling becomes intractable.
### Simulation-Based Approaches
Monte Carlo methods generate data through repeated random sampling based on defined probability models. Agent-based modelling creates synthetic datasets by simulating individual actors following behavioural rules, producing emergent patterns that mirror real system dynamics. Physics-informed simulations and 3D environment rendering generate annotated datasets for autonomous systems, robotics, and computer vision. These approaches produce perfectly labelled training data for scenarios that would be dangerous, expensive, or impossible to capture from real environments. For blockchain applications, simulation-based approaches can model network behaviour, transaction propagation, and smart contract execution. DeFi protocol testing benefits from simulated market conditions, liquidation cascades, and multi-step transaction sequences that stress-test behaviour under extreme scenarios.
These three technical foundations - statistical, ML-based, and simulation-driven - often combine in production systems, with the choice depending on data type, fidelity requirements, and computational constraints.
## Synthetic Data Generation Techniques and Implementation
Practical implementation requires selecting appropriate generative models and integrating them into development workflows. Here's what development teams need to know when moving from theory to production.
### Generative AI Models
**Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)** pit two neural networks against each other: a generator that creates synthetic samples and a discriminator that learns to distinguish generated data from real data. This adversarial dynamic iteratively refines output until the synthetic data becomes statistically indistinguishable from the original. GANs are powerful but can suffer from training instability and mode collapse, where the generator learns to produce only a narrow range of outputs.
**Variational Autoencoders (VAEs)** encode data into a compressed latent space and learn probabilistic mappings that enable sampling of new data points. VAEs offer more stable training than GANs and provide smooth interpolation between data samples, making them well-suited to applications where diversity and controllability matter.
**Transformer-based models** - including large language models like GPT-4o - are increasingly applied to tabular and structured data generation by treating rows or records as sequences and learning dependencies across columns. These models excel at capturing long-range relationships and can be prompted with chain-of-thought reasoning to produce contextually accurate, culturally authentic outputs - a technique we used to great effect in the Panenka AI project (more on that below).
General implementation workflow:
1. **Train the base model** on the original dataset with appropriate preprocessing and validation splits
2. **Configure generation parameters** and constraints (privacy budgets, value ranges, referential integrity rules)
3. **Generate synthetic samples** in batches, monitoring for mode collapse or distribution drift
4. **Validate output quality** through statistical fidelity metrics and downstream task performance
5. **Deploy the synthetic dataset** with appropriate documentation and lineage tracking
### Framework Comparison
| **Framework** | **Best For** | **Complexity** | **Notes** |
| --- | --- | --- | --- |
| TensorFlow / Keras | Custom GAN/VAE architectures, deep learning | High | Custom implementation required |
| Scikit-learn | Statistical methods, rapid prototyping | Medium | Standard tabular formats |
| Synthetic Data Vault (SDV) | Relational databases, tabular data | Low | Good for financial data structures |
| CTGAN | Mixed data types, complex distributions | Medium | Effective for transaction patterns |
Selecting the right tools depends on data complexity, team ML expertise, and pipeline integration requirements. For teams new to synthetic data, the Synthetic Data Vault offers accessible APIs. Teams with established ML infrastructure may prefer CTGAN or custom GAN implementations for greater control. For novel multi-modal requirements - like generating images, names, and behavioural patterns together - custom engineering is typically the only viable path.
## Real-World Example: Panenka AI - Gaming Synthetic Data at Scale
Panenka, an AI-powered football manager game, needed to generate 20,000+ unique player profiles - each with culturally diverse and realistic names from different countries, photorealistic faces with distinct features, and consistent ageing progression throughout a player's career, all without copyright violations or privacy concerns.
This is exactly where off-the-shelf synthetic data platforms hit their limits:
* Generic name generators produced repetitive, culturally inauthentic names and collided with famous footballers
* Basic image generation tools produced inconsistent outputs with no ageing capability
* Standard synthetic data platforms are built for structured tabular data, not multi-modal gaming assets
Our custom solution combined GPT-4o with Chain of Thought prompting and Self Consistency to generate culturally relevant names based on nationality - accounting for each country's diversity and cultural nuance while avoiding famous name combinations. For faces, we developed a 'genetic' approach: building detailed lists of facial element descriptors (lips, noses, eyebrows, cheekbones, freckles), then used GPT-4o to translate these into structured prompts that Leonardo.ai could process effectively. Player ageing was achieved by storing the original generation parameters (prompt, seed, and settings), ensuring appearance consistency as players progressed through their careers.
**The result:** a fully scalable, privacy-safe synthetic data pipeline purpose-built for an entertainment product that no existing platform could have delivered. [Read the full case study here.](https://www.rumblefish.dev/case-studies/panenka/)
## Common Challenges and Solutions
Implementing synthetic data generation in production environments surfaces practical obstacles that development teams must address systematically.
### Data Quality and Fidelity
Generated data quality depends on how well synthetic datasets preserve the statistical properties of real data while maintaining utility for downstream tasks. Implement validation using multiple metrics: Kolmogorov-Smirnov tests for distribution matching, correlation matrix comparisons for relationship preservation, and downstream task performance parity.
High-quality data generation requires domain expert review alongside automated validation. A/B testing between synthetic and real data in non-critical applications can reveal subtle fidelity gaps that statistical tests alone may miss. Treat synthetic data quality as an ongoing process, not a one-time checkpoint.
### Scalability and Performance
Generating realistic synthetic data at enterprise scale, billions of records with complex interdependencies, strains computational resources. Optimise generation pipelines through distributed computing frameworks that parallelise independent generation tasks. Implement incremental generation strategies that produce data on demand rather than pre-generating massive datasets. Cloud infrastructure with auto-scaling (AWS is our stack of choice) enables burst capacity for load and performance testing scenarios that require high volumes.
### Regulatory Compliance and Privacy
While synthetic data eliminates direct privacy risks, regulators increasingly scrutinise generation processes. Establish differential privacy methods that provide mathematical guarantees on information leakage. Document generation methodology, training data sources, and validation results to demonstrate compliance.
For GDPR, CCPA, and industry-specific regulations, maintain audit trails showing that no sensitive data persists in synthetic outputs. For high-stakes applications in healthcare or finance, consider third-party validation of your generation processes. Properly implemented synthetic data is one of the most robust privacy-preserving strategies available - but "properly implemented" is doing a lot of work in that sentence.
### Custom Engineering vs. Off-the-Shelf Platforms
This is a question we get often. Platforms like Gretel, MOSTLY AI, and Tonic are excellent for common use cases involving structured tabular data. They're quick to set up and require no ML expertise. But they have hard limits.
When your requirements are complex, multi-modal, or domain-specific, **custom engineering pays for itself.** Here's how the two approaches compare:
| | **Synthetic Data Platforms** | **Rumble Fish Custom Engineering** |
| --- | --- | --- |
| **Data scope** | Structured/tabular data primarily | Multi-modal: text, images, video, structured data |
| **Customization** | Configure pre-built generators | Engineer solutions for your exact requirements |
| **Industry fit** | Generic templates | Domain-specific intelligence built in |
| **Support model** | Self-service (you figure it out) | True partnership - we take full ownership |
| **Pricing** | Subscription per row/GB | Project-based - you own the solution |
| **Edge cases** | Works for common scenarios | Excels at complex, novel requirements |
The right choice depends on your requirements. If a platform fits your use case, use it. If it doesn't, that's where we come in.
## Conclusion and Next Steps
Synthetic data generation provides a privacy-preserving solution for modern development challenges, enabling teams to build and test AI systems without exposing sensitive production data. The technology bridges the gap between data utility requirements and regulatory compliance, while addressing fundamental problems of data scarcity and acquisition costs.
**Immediate actionable steps:**
* Assess your current data constraints: identify where access restrictions or scarcity limit development velocity or model performance
* Pilot with a bounded use case: start with test data generation for a single service to build organisational familiarity
* Evaluate tools against your requirements: match your data types and technical needs against available frameworks and platforms
* Consider whether your requirements fall outside what platforms can handle - if so, custom engineering is worth exploring
---
### Your product deserves synthetic data engineered for it
Whether you're building the next innovative product, training specialised AI models, or solving unique data challenges, generic platforms often won't cut it. You bring the product vision. We bring the product-building expertise - battle-tested technology, true partnership, and the engineering depth to solve problems platforms can't touch.
Get in touch: [hello@rumblefish.dev](mailto:hello@rumblefish.dev) | [Read about Synthetic Data Generation services](https://www.rumblefish.dev/services/synthetic-data-generation/)
Synthetic Data Generation: A Complete Guide for 2026If you're building AI models, running software tests, or navigating the maze of data privacy compliance, you've probably run into the same wall: the data you need is either locked away, too expensive to collect, or legally off-limits. Synthetic data generation is how the smartest teams are breaking through that wall - and in this guide, we'll show you exactly how it works.
Synthetic data generation is the process of creating artificial datasets that replicate the statistical properties, patterns, and correlations of real-world data without incorporating any actual individual records or sensitive information. This technology has become essential for organisations navigating the intersection of data-driven innovation and privacy compliance. At Rumble Fish, we've seen this challenge play out across DeFi protocols, fintech platforms, and AI-powered products. Whether you're simulating on-chain transaction behaviour, generating training data for ML models, or stress-testing a financial system, synthetic data is no longer a workaround - it's a battle-tested strategy.
---
**TL;DR**
Synthetic data generation uses algorithms, statistical models, and AI techniques to create artificial data that preserves the statistical properties of real data while eliminating privacy risks. The generation process analyses original data patterns and recreates them as entirely new data points that contain no traceable personal information.
---
After reading this guide, you will understand:
* How synthetic data generation processes work at a technical level
* The different types of synthetic data and their specific applications
* Which tools and frameworks fit your use case
* How to address data quality, scalability, and compliance challenges
* Practical steps to implement synthetic data in your development workflow
* Why custom engineering often beats off-the-shelf platforms - and when to use each
## Understanding Synthetic Data Generation
Synthetic data generation refers to **creating artificial data that maintains the utility and statistical characteristics of existing data** without exposing sensitive production data. This artificially generated data serves as a privacy-preserving alternative for AI training, test data generation, analytics, and simulations across industries. For modern software development teams, the ability to generate synthetic data solves several critical problems: data scarcity in underrepresented scenarios, privacy restrictions on production data access, and the high costs of acquiring and labelling real data. Data scientists can train robust machine learning models, run load and performance tests, and develop new features without ever touching actual sensitive information.
### Types of Synthetic Data
**Structured synthetic data** includes tabular data, relational database records, and financial transaction logs. This type is particularly valuable for fintech applications where generating realistic tabular data enables fraud detection model training and payment system testing without exposing real customer data to risk.
**Unstructured data** encompasses images, text, audio, and video generated through deep learning models. Natural language processing applications benefit from synthetic text that mimics real communication patterns, while computer vision systems train on generated images representing scenarios difficult to capture in production.
**Time-series synthetic data** covers sensor readings, transaction logs, market data, and sequential events. For blockchain and DeFi applications, this includes simulated on-chain activity, protocol interactions, and smart contract transaction patterns that would be impossible to collect at scale from live networks.
Each type connects to specific development needs: structured formats support database testing and analytics, unstructured formats enable AI model training, and time-series data powers simulation and performance testing.
### Synthetic vs. Real vs. Anonymised Data
Traditional anonymisation techniques - data masking, tokenisation, generalisation - modify real data to obscure identities. However, these approaches carry re-identification risks when combined with external datasets, and often degrade data utility by removing the contextual information essential for analysis. Synthetic data fundamentally differs because **it contains no actual data from real individuals**. The generator creates data that is statistically identical to the source but shares zero one-to-one correspondence with original records. This distinction matters significantly for regulatory compliance: while anonymised data may still fall under GDPR or HIPAA scope if re-identification is possible, properly generated synthetic data typically does not. The utility preservation advantage is equally important. Anonymisation often destroys the correlations and statistical relationships needed for meaningful analysis. **Synthetic data maintains these patterns - mean, variance, multivariate dependencies - while eliminating privacy risks entirely.**
## How Synthetic Data Generation Works
The synthetic data generation workflow follows a consistent arc: analyse source data to extract patterns, build models that capture those patterns, and generate new data points that embody the learned characteristics without reproducing original records. The sophistication of each step determines the quality and utility of the resulting synthetic datasets.
### Statistical Distribution Modelling
Statistical approaches form the foundation of many synthetic data generation pipelines. The process begins with analysing the probability distributions present in the original data - identifying whether variables follow Gaussian, uniform, exponential, or custom distributions, and estimating their parameters.
Copula models extend this by capturing multivariate dependencies between variables. Rather than assuming independence or simple correlations, copulas model the joint distribution structure, enabling the generation of data samples that honour complex relationships between columns in tabular data - critical when, for example, a synthetic financial transaction needs to respect correlations between amount, merchant category, and time of day. These methods excel when interpretability matters and when data relationships are well-understood. Implementation complexity varies: univariate distribution matching is straightforward, while accurately modelling high-dimensional dependencies requires careful statistical validation.
### Machine Learning-Based Generation
Machine learning models learn patterns from training data through supervised and unsupervised approaches. Neural networks, particularly deep learning models, capture non-linear relationships and complex feature interactions that statistical methods can miss. Supervised approaches train on labelled datasets to generate synthetic data with known properties. Unsupervised methods discover latent structure in unlabelled data, enabling the generation of realistic data that reflects inherent patterns without explicit specification. **The relationship between ML and statistical methods is complementary:** statistical techniques provide interpretable baselines and work well for structured formats, while ML approaches handle the complexity of unstructured data and high-dimensional feature spaces where explicit modelling becomes intractable.
### Simulation-Based Approaches
Monte Carlo methods generate data through repeated random sampling based on defined probability models. Agent-based modelling creates synthetic datasets by simulating individual actors following behavioural rules, producing emergent patterns that mirror real system dynamics. Physics-informed simulations and 3D environment rendering generate annotated datasets for autonomous systems, robotics, and computer vision. These approaches produce perfectly labelled training data for scenarios that would be dangerous, expensive, or impossible to capture from real environments. For blockchain applications, simulation-based approaches can model network behaviour, transaction propagation, and smart contract execution. DeFi protocol testing benefits from simulated market conditions, liquidation cascades, and multi-step transaction sequences that stress-test behaviour under extreme scenarios.
These three technical foundations - statistical, ML-based, and simulation-driven - often combine in production systems, with the choice depending on data type, fidelity requirements, and computational constraints.
## Synthetic Data Generation Techniques and Implementation
Practical implementation requires selecting appropriate generative models and integrating them into development workflows. Here's what development teams need to know when moving from theory to production.
### Generative AI Models
**Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)** pit two neural networks against each other: a generator that creates synthetic samples and a discriminator that learns to distinguish generated data from real data. This adversarial dynamic iteratively refines output until the synthetic data becomes statistically indistinguishable from the original. GANs are powerful but can suffer from training instability and mode collapse, where the generator learns to produce only a narrow range of outputs.
**Variational Autoencoders (VAEs)** encode data into a compressed latent space and learn probabilistic mappings that enable sampling of new data points. VAEs offer more stable training than GANs and provide smooth interpolation between data samples, making them well-suited to applications where diversity and controllability matter.
**Transformer-based models** - including large language models like GPT-4o - are increasingly applied to tabular and structured data generation by treating rows or records as sequences and learning dependencies across columns. These models excel at capturing long-range relationships and can be prompted with chain-of-thought reasoning to produce contextually accurate, culturally authentic outputs - a technique we used to great effect in the Panenka AI project (more on that below).
General implementation workflow:
1. **Train the base model** on the original dataset with appropriate preprocessing and validation splits
2. **Configure generation parameters** and constraints (privacy budgets, value ranges, referential integrity rules)
3. **Generate synthetic samples** in batches, monitoring for mode collapse or distribution drift
4. **Validate output quality** through statistical fidelity metrics and downstream task performance
5. **Deploy the synthetic dataset** with appropriate documentation and lineage tracking
### Framework Comparison
| **Framework** | **Best For** | **Complexity** | **Notes** |
| --- | --- | --- | --- |
| TensorFlow / Keras | Custom GAN/VAE architectures, deep learning | High | Custom implementation required |
| Scikit-learn | Statistical methods, rapid prototyping | Medium | Standard tabular formats |
| Synthetic Data Vault (SDV) | Relational databases, tabular data | Low | Good for financial data structures |
| CTGAN | Mixed data types, complex distributions | Medium | Effective for transaction patterns |
Selecting the right tools depends on data complexity, team ML expertise, and pipeline integration requirements. For teams new to synthetic data, the Synthetic Data Vault offers accessible APIs. Teams with established ML infrastructure may prefer CTGAN or custom GAN implementations for greater control. For novel multi-modal requirements - like generating images, names, and behavioural patterns together - custom engineering is typically the only viable path.
## Real-World Example: Panenka AI - Gaming Synthetic Data at Scale
Panenka, an AI-powered football manager game, needed to generate 20,000+ unique player profiles - each with culturally diverse and realistic names from different countries, photorealistic faces with distinct features, and consistent ageing progression throughout a player's career, all without copyright violations or privacy concerns.
This is exactly where off-the-shelf synthetic data platforms hit their limits:
* Generic name generators produced repetitive, culturally inauthentic names and collided with famous footballers
* Basic image generation tools produced inconsistent outputs with no ageing capability
* Standard synthetic data platforms are built for structured tabular data, not multi-modal gaming assets
Our custom solution combined GPT-4o with Chain of Thought prompting and Self Consistency to generate culturally relevant names based on nationality - accounting for each country's diversity and cultural nuance while avoiding famous name combinations. For faces, we developed a 'genetic' approach: building detailed lists of facial element descriptors (lips, noses, eyebrows, cheekbones, freckles), then used GPT-4o to translate these into structured prompts that Leonardo.ai could process effectively. Player ageing was achieved by storing the original generation parameters (prompt, seed, and settings), ensuring appearance consistency as players progressed through their careers.
**The result:** a fully scalable, privacy-safe synthetic data pipeline purpose-built for an entertainment product that no existing platform could have delivered. [Read the full case study here.](https://www.rumblefish.dev/case-studies/panenka/)
## Common Challenges and Solutions
Implementing synthetic data generation in production environments surfaces practical obstacles that development teams must address systematically.
### Data Quality and Fidelity
Generated data quality depends on how well synthetic datasets preserve the statistical properties of real data while maintaining utility for downstream tasks. Implement validation using multiple metrics: Kolmogorov-Smirnov tests for distribution matching, correlation matrix comparisons for relationship preservation, and downstream task performance parity.
High-quality data generation requires domain expert review alongside automated validation. A/B testing between synthetic and real data in non-critical applications can reveal subtle fidelity gaps that statistical tests alone may miss. Treat synthetic data quality as an ongoing process, not a one-time checkpoint.
### Scalability and Performance
Generating realistic synthetic data at enterprise scale, billions of records with complex interdependencies, strains computational resources. Optimise generation pipelines through distributed computing frameworks that parallelise independent generation tasks. Implement incremental generation strategies that produce data on demand rather than pre-generating massive datasets. Cloud infrastructure with auto-scaling (AWS is our stack of choice) enables burst capacity for load and performance testing scenarios that require high volumes.
### Regulatory Compliance and Privacy
While synthetic data eliminates direct privacy risks, regulators increasingly scrutinise generation processes. Establish differential privacy methods that provide mathematical guarantees on information leakage. Document generation methodology, training data sources, and validation results to demonstrate compliance.
For GDPR, CCPA, and industry-specific regulations, maintain audit trails showing that no sensitive data persists in synthetic outputs. For high-stakes applications in healthcare or finance, consider third-party validation of your generation processes. Properly implemented synthetic data is one of the most robust privacy-preserving strategies available - but "properly implemented" is doing a lot of work in that sentence.
### Custom Engineering vs. Off-the-Shelf Platforms
This is a question we get often. Platforms like Gretel, MOSTLY AI, and Tonic are excellent for common use cases involving structured tabular data. They're quick to set up and require no ML expertise. But they have hard limits.
When your requirements are complex, multi-modal, or domain-specific, **custom engineering pays for itself.** Here's how the two approaches compare:
| | **Synthetic Data Platforms** | **Rumble Fish Custom Engineering** |
| --- | --- | --- |
| **Data scope** | Structured/tabular data primarily | Multi-modal: text, images, video, structured data |
| **Customization** | Configure pre-built generators | Engineer solutions for your exact requirements |
| **Industry fit** | Generic templates | Domain-specific intelligence built in |
| **Support model** | Self-service (you figure it out) | True partnership - we take full ownership |
| **Pricing** | Subscription per row/GB | Project-based - you own the solution |
| **Edge cases** | Works for common scenarios | Excels at complex, novel requirements |
The right choice depends on your requirements. If a platform fits your use case, use it. If it doesn't, that's where we come in.
## Conclusion and Next Steps
Synthetic data generation provides a privacy-preserving solution for modern development challenges, enabling teams to build and test AI systems without exposing sensitive production data. The technology bridges the gap between data utility requirements and regulatory compliance, while addressing fundamental problems of data scarcity and acquisition costs.
**Immediate actionable steps:**
* Assess your current data constraints: identify where access restrictions or scarcity limit development velocity or model performance
* Pilot with a bounded use case: start with test data generation for a single service to build organisational familiarity
* Evaluate tools against your requirements: match your data types and technical needs against available frameworks and platforms
* Consider whether your requirements fall outside what platforms can handle - if so, custom engineering is worth exploring
---
### Your product deserves synthetic data engineered for it
Whether you're building the next innovative product, training specialised AI models, or solving unique data challenges, generic platforms often won't cut it. You bring the product vision. We bring the product-building expertise - battle-tested technology, true partnership, and the engineering depth to solve problems platforms can't touch.
Get in touch: [hello@rumblefish.dev](mailto:hello@rumblefish.dev) | [Read about Synthetic Data Generation services](https://www.rumblefish.dev/services/synthetic-data-generation/) Running Claude as a Backend Service: How We Build AI-Powered Web Applications on AWS
Running Claude as a Backend Service: How We Build AI-Powered Web Applications on AWS By Marek KowalskiThe AI revolution is transforming how we build software. But there's a gap between the impressive capabilities of large language models and the practical expectations of business users who need familiar, reliable interfaces. At Rumble Fish, we've developed an architecture that bridges this gap - running Claude as a backend microservice that powers traditional-looking web applications with AI-driven intelligence.
## The Traditional Way: Claude as a Developer Tool
Most developers know Claude as either a built-in code assistant in popular IDEs like VS Code or Cursor, or as a standalone desktop application where you type prompts and get responses. These interfaces work great for technical users who are comfortable with conversational AI. But what about everyone else?
## The Challenge: AI for Non-Technical Users
At Rumble Fish, we've seen growing interest from clients who want to automate work that requires thinking and creativity - tasks that go beyond simple rule-based automation. Content analysis, document processing, research synthesis, and decision support - these are areas where AI excels.
**The challenge?** Most business users expect traditional browser-based interfaces. They're not comfortable typing prompts into a chat window and interpreting unstructured responses. They want buttons, forms, dashboards, and predictable workflows. How do we reconcile the creative, flexible nature of AI agents with the structured expectations of enterprise software?
## Our Solution: Claude as a Microservice
We run Claude as a containerized service on AWS. Here's how it works:
### The Container Setup
We package Claude using the Claude SDK inside a Docker container, deployed as an ECS task. Each container includes:
\- A checkout of a repository containing a \`CLAUDE.md\` file
\- Skill definitions and scripts specific to the client's use case
\- All the context the agent needs to perform its specialized tasks
The \`CLAUDE.md\` file acts as the agent's instruction manual - defining its role, output formats, and behavioral guidelines. This gives us precise control over how the agent operates while maintaining the flexibility that makes AI valuable.
### Persistence Through S3 Sync
At the start and end of each task, we run \`aws s3 sync\` to synchronize the agent's working directory with an S3 bucket. This simple mechanism provides:
\- **State persistence**: The agent accumulates knowledge between invocations
\- **Audit trail**: Every file the agent creates is preserved
\- **Easy integration**: Other services can read the agent's outputs directly from S3
## The Architecture in Detail
When a user interacts with our web interface, here's the sequence of events:
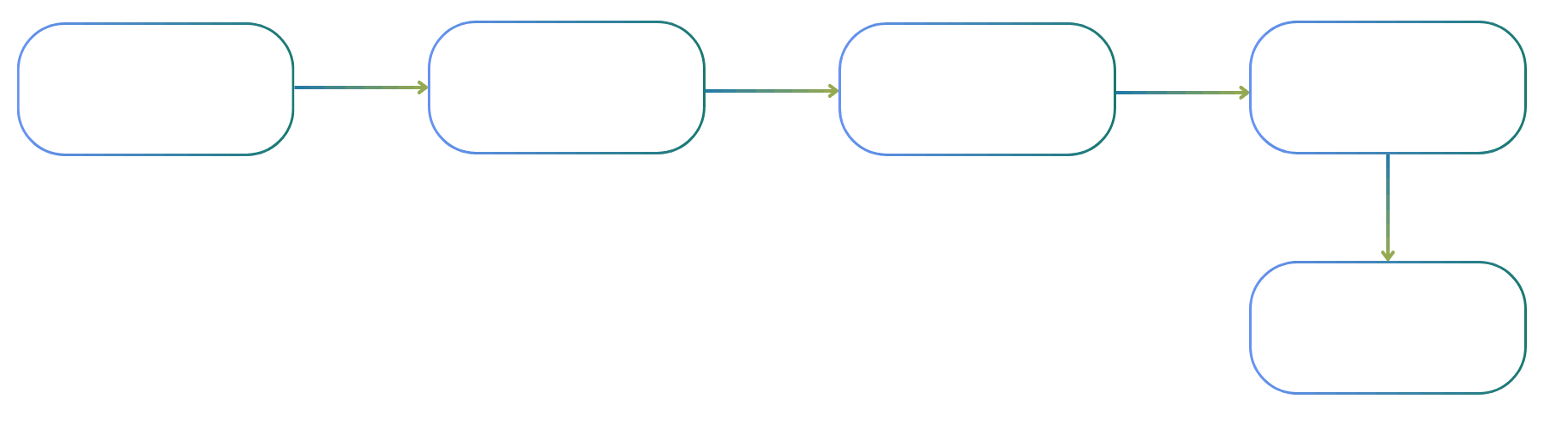
1. **User Action:** The user clicks a button or submits a form in our React Admin interface
2. **Backend Processing:** A Lambda function (exposed via API Gateway) receives the request and constructs a prompt for the agent
3. **Queue Management:** The prompt goes into an SQS FIFO queue, ensuring ordered processing and preventing concurrent executions
4. **Agent Execution:** An ECS task spins up, the agent processes the prompt, and generates its outputs
5. **Result Storage:** Output files are synced back to S3, task metadata (ARNs, status) is stored in our database, and logs end up in another S3 bucket
### Why SQS FIFO?
The FIFO queue is crucial. While the agent is running, queue consumption is blocked. This prevents race conditions and ensures the agent always works with a consistent state. It also gives us natural backpressure - if requests come in faster than the agent can process them, they queue up gracefully.
### Structured Output, Flexible Presentation
We instruct the agent (via \`CLAUDE.md\`) to save its analysis in markdown format at predictable locations. This gives us:
\- **No custom UI development:** Markdown renders beautifully with minimal effort
\- **Flexibility:** The agent can structure its output however makes sense for the task
\- **Readability**: Non-technical users can read and understand the results directly
The admin interface simply presents the contents of the S3 bucket. It doesn't need to understand what the agent does; it just displays what the agent produces.
## The Result: AI That Feels Like Software
The end product looks and feels like a standard web application. Users see familiar interfaces - lists, forms, buttons, dashboards. They don't need to learn prompt engineering or understand how AI works. But behind that familiar facade, Claude is doing work that would be impossible with traditional software: synthesizing information, making judgment calls, generating creative solutions, and adapting to edge cases that no developer anticipated.
It's the best of both worlds: the reliability and usability of traditional software, combined with the intelligence and adaptability of modern AI.
## Proven in Production
At Rumble Fish, we're currently running three different projects using this architecture. Each solves a different problem, but they share the same pattern:
* Automate work that requires thinking, not just data shuffling
* Present results through interfaces that traditional users understand
* Maintain full auditability and control over the AI's behavior
This approach is becoming our go-to solution for a wide range of problems. The common thread: bridging intelligent automation with familiar user experiences.
## Is This Right for Your Organization?
If your team is exploring AI adoption but worried about user acceptance, complex integrations, or unpredictable behavior, **this architecture might be the answer.** It lets you harness AI capabilities while maintaining the control and predictability that enterprise environments demand.
**Thinking about bringing AI into your workflows?** [Book a free consultation](https://rumblefish.dev/contact) with our team. We'll help you identify opportunities and design an approach that fits your needs.
By Marek KowalskiThe AI revolution is transforming how we build software. But there's a gap between the impressive capabilities of large language models and the practical expectations of business users who need familiar, reliable interfaces. At Rumble Fish, we've developed an architecture that bridges this gap - running Claude as a backend microservice that powers traditional-looking web applications with AI-driven intelligence.
## The Traditional Way: Claude as a Developer Tool
Most developers know Claude as either a built-in code assistant in popular IDEs like VS Code or Cursor, or as a standalone desktop application where you type prompts and get responses. These interfaces work great for technical users who are comfortable with conversational AI. But what about everyone else?
## The Challenge: AI for Non-Technical Users
At Rumble Fish, we've seen growing interest from clients who want to automate work that requires thinking and creativity - tasks that go beyond simple rule-based automation. Content analysis, document processing, research synthesis, and decision support - these are areas where AI excels.
**The challenge?** Most business users expect traditional browser-based interfaces. They're not comfortable typing prompts into a chat window and interpreting unstructured responses. They want buttons, forms, dashboards, and predictable workflows. How do we reconcile the creative, flexible nature of AI agents with the structured expectations of enterprise software?
## Our Solution: Claude as a Microservice
We run Claude as a containerized service on AWS. Here's how it works:
### The Container Setup
We package Claude using the Claude SDK inside a Docker container, deployed as an ECS task. Each container includes:
\- A checkout of a repository containing a \`CLAUDE.md\` file
\- Skill definitions and scripts specific to the client's use case
\- All the context the agent needs to perform its specialized tasks
The \`CLAUDE.md\` file acts as the agent's instruction manual - defining its role, output formats, and behavioral guidelines. This gives us precise control over how the agent operates while maintaining the flexibility that makes AI valuable.
### Persistence Through S3 Sync
At the start and end of each task, we run \`aws s3 sync\` to synchronize the agent's working directory with an S3 bucket. This simple mechanism provides:
\- **State persistence**: The agent accumulates knowledge between invocations
\- **Audit trail**: Every file the agent creates is preserved
\- **Easy integration**: Other services can read the agent's outputs directly from S3
## The Architecture in Detail
When a user interacts with our web interface, here's the sequence of events:

1. **User Action:** The user clicks a button or submits a form in our React Admin interface
2. **Backend Processing:** A Lambda function (exposed via API Gateway) receives the request and constructs a prompt for the agent
3. **Queue Management:** The prompt goes into an SQS FIFO queue, ensuring ordered processing and preventing concurrent executions
4. **Agent Execution:** An ECS task spins up, the agent processes the prompt, and generates its outputs
5. **Result Storage:** Output files are synced back to S3, task metadata (ARNs, status) is stored in our database, and logs end up in another S3 bucket
### Why SQS FIFO?
The FIFO queue is crucial. While the agent is running, queue consumption is blocked. This prevents race conditions and ensures the agent always works with a consistent state. It also gives us natural backpressure - if requests come in faster than the agent can process them, they queue up gracefully.
### Structured Output, Flexible Presentation
We instruct the agent (via \`CLAUDE.md\`) to save its analysis in markdown format at predictable locations. This gives us:
\- **No custom UI development:** Markdown renders beautifully with minimal effort
\- **Flexibility:** The agent can structure its output however makes sense for the task
\- **Readability**: Non-technical users can read and understand the results directly
The admin interface simply presents the contents of the S3 bucket. It doesn't need to understand what the agent does; it just displays what the agent produces.
## The Result: AI That Feels Like Software
The end product looks and feels like a standard web application. Users see familiar interfaces - lists, forms, buttons, dashboards. They don't need to learn prompt engineering or understand how AI works. But behind that familiar facade, Claude is doing work that would be impossible with traditional software: synthesizing information, making judgment calls, generating creative solutions, and adapting to edge cases that no developer anticipated.
It's the best of both worlds: the reliability and usability of traditional software, combined with the intelligence and adaptability of modern AI.
## Proven in Production
At Rumble Fish, we're currently running three different projects using this architecture. Each solves a different problem, but they share the same pattern:
* Automate work that requires thinking, not just data shuffling
* Present results through interfaces that traditional users understand
* Maintain full auditability and control over the AI's behavior
This approach is becoming our go-to solution for a wide range of problems. The common thread: bridging intelligent automation with familiar user experiences.
## Is This Right for Your Organization?
If your team is exploring AI adoption but worried about user acceptance, complex integrations, or unpredictable behavior, **this architecture might be the answer.** It lets you harness AI capabilities while maintaining the control and predictability that enterprise environments demand.
**Thinking about bringing AI into your workflows?** [Book a free consultation](https://rumblefish.dev/contact) with our team. We'll help you identify opportunities and design an approach that fits your needs.
Check a piece of expert knowledge
 Synthetic Data Generation: A Complete Guide for 2026If you're building AI models, running software tests, or navigating the maze of data privacy compliance, you've probably run into the same wall: the data you need is either locked away, too expensive to collect, or legally off-limits. Synthetic data generation is how the smartest teams are breaking through that wall - and in this guide, we'll show you exactly how it works.
Synthetic data generation is the process of creating artificial datasets that replicate the statistical properties, patterns, and correlations of real-world data without incorporating any actual individual records or sensitive information. This technology has become essential for organisations navigating the intersection of data-driven innovation and privacy compliance. At Rumble Fish, we've seen this challenge play out across DeFi protocols, fintech platforms, and AI-powered products. Whether you're simulating on-chain transaction behaviour, generating training data for ML models, or stress-testing a financial system, synthetic data is no longer a workaround - it's a battle-tested strategy.
---
**TL;DR**
Synthetic data generation uses algorithms, statistical models, and AI techniques to create artificial data that preserves the statistical properties of real data while eliminating privacy risks. The generation process analyses original data patterns and recreates them as entirely new data points that contain no traceable personal information.
---
After reading this guide, you will understand:
* How synthetic data generation processes work at a technical level
* The different types of synthetic data and their specific applications
* Which tools and frameworks fit your use case
* How to address data quality, scalability, and compliance challenges
* Practical steps to implement synthetic data in your development workflow
* Why custom engineering often beats off-the-shelf platforms - and when to use each
## Understanding Synthetic Data Generation
Synthetic data generation refers to **creating artificial data that maintains the utility and statistical characteristics of existing data** without exposing sensitive production data. This artificially generated data serves as a privacy-preserving alternative for AI training, test data generation, analytics, and simulations across industries. For modern software development teams, the ability to generate synthetic data solves several critical problems: data scarcity in underrepresented scenarios, privacy restrictions on production data access, and the high costs of acquiring and labelling real data. Data scientists can train robust machine learning models, run load and performance tests, and develop new features without ever touching actual sensitive information.
### Types of Synthetic Data
**Structured synthetic data** includes tabular data, relational database records, and financial transaction logs. This type is particularly valuable for fintech applications where generating realistic tabular data enables fraud detection model training and payment system testing without exposing real customer data to risk.
**Unstructured data** encompasses images, text, audio, and video generated through deep learning models. Natural language processing applications benefit from synthetic text that mimics real communication patterns, while computer vision systems train on generated images representing scenarios difficult to capture in production.
**Time-series synthetic data** covers sensor readings, transaction logs, market data, and sequential events. For blockchain and DeFi applications, this includes simulated on-chain activity, protocol interactions, and smart contract transaction patterns that would be impossible to collect at scale from live networks.
Each type connects to specific development needs: structured formats support database testing and analytics, unstructured formats enable AI model training, and time-series data powers simulation and performance testing.
### Synthetic vs. Real vs. Anonymised Data
Traditional anonymisation techniques - data masking, tokenisation, generalisation - modify real data to obscure identities. However, these approaches carry re-identification risks when combined with external datasets, and often degrade data utility by removing the contextual information essential for analysis. Synthetic data fundamentally differs because **it contains no actual data from real individuals**. The generator creates data that is statistically identical to the source but shares zero one-to-one correspondence with original records. This distinction matters significantly for regulatory compliance: while anonymised data may still fall under GDPR or HIPAA scope if re-identification is possible, properly generated synthetic data typically does not. The utility preservation advantage is equally important. Anonymisation often destroys the correlations and statistical relationships needed for meaningful analysis. **Synthetic data maintains these patterns - mean, variance, multivariate dependencies - while eliminating privacy risks entirely.**
## How Synthetic Data Generation Works
The synthetic data generation workflow follows a consistent arc: analyse source data to extract patterns, build models that capture those patterns, and generate new data points that embody the learned characteristics without reproducing original records. The sophistication of each step determines the quality and utility of the resulting synthetic datasets.
### Statistical Distribution Modelling
Statistical approaches form the foundation of many synthetic data generation pipelines. The process begins with analysing the probability distributions present in the original data - identifying whether variables follow Gaussian, uniform, exponential, or custom distributions, and estimating their parameters.
Copula models extend this by capturing multivariate dependencies between variables. Rather than assuming independence or simple correlations, copulas model the joint distribution structure, enabling the generation of data samples that honour complex relationships between columns in tabular data - critical when, for example, a synthetic financial transaction needs to respect correlations between amount, merchant category, and time of day. These methods excel when interpretability matters and when data relationships are well-understood. Implementation complexity varies: univariate distribution matching is straightforward, while accurately modelling high-dimensional dependencies requires careful statistical validation.
### Machine Learning-Based Generation
Machine learning models learn patterns from training data through supervised and unsupervised approaches. Neural networks, particularly deep learning models, capture non-linear relationships and complex feature interactions that statistical methods can miss. Supervised approaches train on labelled datasets to generate synthetic data with known properties. Unsupervised methods discover latent structure in unlabelled data, enabling the generation of realistic data that reflects inherent patterns without explicit specification. **The relationship between ML and statistical methods is complementary:** statistical techniques provide interpretable baselines and work well for structured formats, while ML approaches handle the complexity of unstructured data and high-dimensional feature spaces where explicit modelling becomes intractable.
### Simulation-Based Approaches
Monte Carlo methods generate data through repeated random sampling based on defined probability models. Agent-based modelling creates synthetic datasets by simulating individual actors following behavioural rules, producing emergent patterns that mirror real system dynamics. Physics-informed simulations and 3D environment rendering generate annotated datasets for autonomous systems, robotics, and computer vision. These approaches produce perfectly labelled training data for scenarios that would be dangerous, expensive, or impossible to capture from real environments. For blockchain applications, simulation-based approaches can model network behaviour, transaction propagation, and smart contract execution. DeFi protocol testing benefits from simulated market conditions, liquidation cascades, and multi-step transaction sequences that stress-test behaviour under extreme scenarios.
These three technical foundations - statistical, ML-based, and simulation-driven - often combine in production systems, with the choice depending on data type, fidelity requirements, and computational constraints.
## Synthetic Data Generation Techniques and Implementation
Practical implementation requires selecting appropriate generative models and integrating them into development workflows. Here's what development teams need to know when moving from theory to production.
### Generative AI Models
**Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)** pit two neural networks against each other: a generator that creates synthetic samples and a discriminator that learns to distinguish generated data from real data. This adversarial dynamic iteratively refines output until the synthetic data becomes statistically indistinguishable from the original. GANs are powerful but can suffer from training instability and mode collapse, where the generator learns to produce only a narrow range of outputs.
**Variational Autoencoders (VAEs)** encode data into a compressed latent space and learn probabilistic mappings that enable sampling of new data points. VAEs offer more stable training than GANs and provide smooth interpolation between data samples, making them well-suited to applications where diversity and controllability matter.
**Transformer-based models** - including large language models like GPT-4o - are increasingly applied to tabular and structured data generation by treating rows or records as sequences and learning dependencies across columns. These models excel at capturing long-range relationships and can be prompted with chain-of-thought reasoning to produce contextually accurate, culturally authentic outputs - a technique we used to great effect in the Panenka AI project (more on that below).
General implementation workflow:
1. **Train the base model** on the original dataset with appropriate preprocessing and validation splits
2. **Configure generation parameters** and constraints (privacy budgets, value ranges, referential integrity rules)
3. **Generate synthetic samples** in batches, monitoring for mode collapse or distribution drift
4. **Validate output quality** through statistical fidelity metrics and downstream task performance
5. **Deploy the synthetic dataset** with appropriate documentation and lineage tracking
### Framework Comparison
| **Framework** | **Best For** | **Complexity** | **Notes** |
| --- | --- | --- | --- |
| TensorFlow / Keras | Custom GAN/VAE architectures, deep learning | High | Custom implementation required |
| Scikit-learn | Statistical methods, rapid prototyping | Medium | Standard tabular formats |
| Synthetic Data Vault (SDV) | Relational databases, tabular data | Low | Good for financial data structures |
| CTGAN | Mixed data types, complex distributions | Medium | Effective for transaction patterns |
Selecting the right tools depends on data complexity, team ML expertise, and pipeline integration requirements. For teams new to synthetic data, the Synthetic Data Vault offers accessible APIs. Teams with established ML infrastructure may prefer CTGAN or custom GAN implementations for greater control. For novel multi-modal requirements - like generating images, names, and behavioural patterns together - custom engineering is typically the only viable path.
## Real-World Example: Panenka AI - Gaming Synthetic Data at Scale
Panenka, an AI-powered football manager game, needed to generate 20,000+ unique player profiles - each with culturally diverse and realistic names from different countries, photorealistic faces with distinct features, and consistent ageing progression throughout a player's career, all without copyright violations or privacy concerns.
This is exactly where off-the-shelf synthetic data platforms hit their limits:
* Generic name generators produced repetitive, culturally inauthentic names and collided with famous footballers
* Basic image generation tools produced inconsistent outputs with no ageing capability
* Standard synthetic data platforms are built for structured tabular data, not multi-modal gaming assets
Our custom solution combined GPT-4o with Chain of Thought prompting and Self Consistency to generate culturally relevant names based on nationality - accounting for each country's diversity and cultural nuance while avoiding famous name combinations. For faces, we developed a 'genetic' approach: building detailed lists of facial element descriptors (lips, noses, eyebrows, cheekbones, freckles), then used GPT-4o to translate these into structured prompts that Leonardo.ai could process effectively. Player ageing was achieved by storing the original generation parameters (prompt, seed, and settings), ensuring appearance consistency as players progressed through their careers.
**The result:** a fully scalable, privacy-safe synthetic data pipeline purpose-built for an entertainment product that no existing platform could have delivered. [Read the full case study here.](https://www.rumblefish.dev/case-studies/panenka/)
## Common Challenges and Solutions
Implementing synthetic data generation in production environments surfaces practical obstacles that development teams must address systematically.
### Data Quality and Fidelity
Generated data quality depends on how well synthetic datasets preserve the statistical properties of real data while maintaining utility for downstream tasks. Implement validation using multiple metrics: Kolmogorov-Smirnov tests for distribution matching, correlation matrix comparisons for relationship preservation, and downstream task performance parity.
High-quality data generation requires domain expert review alongside automated validation. A/B testing between synthetic and real data in non-critical applications can reveal subtle fidelity gaps that statistical tests alone may miss. Treat synthetic data quality as an ongoing process, not a one-time checkpoint.
### Scalability and Performance
Generating realistic synthetic data at enterprise scale, billions of records with complex interdependencies, strains computational resources. Optimise generation pipelines through distributed computing frameworks that parallelise independent generation tasks. Implement incremental generation strategies that produce data on demand rather than pre-generating massive datasets. Cloud infrastructure with auto-scaling (AWS is our stack of choice) enables burst capacity for load and performance testing scenarios that require high volumes.
### Regulatory Compliance and Privacy
While synthetic data eliminates direct privacy risks, regulators increasingly scrutinise generation processes. Establish differential privacy methods that provide mathematical guarantees on information leakage. Document generation methodology, training data sources, and validation results to demonstrate compliance.
For GDPR, CCPA, and industry-specific regulations, maintain audit trails showing that no sensitive data persists in synthetic outputs. For high-stakes applications in healthcare or finance, consider third-party validation of your generation processes. Properly implemented synthetic data is one of the most robust privacy-preserving strategies available - but "properly implemented" is doing a lot of work in that sentence.
### Custom Engineering vs. Off-the-Shelf Platforms
This is a question we get often. Platforms like Gretel, MOSTLY AI, and Tonic are excellent for common use cases involving structured tabular data. They're quick to set up and require no ML expertise. But they have hard limits.
When your requirements are complex, multi-modal, or domain-specific, **custom engineering pays for itself.** Here's how the two approaches compare:
| | **Synthetic Data Platforms** | **Rumble Fish Custom Engineering** |
| --- | --- | --- |
| **Data scope** | Structured/tabular data primarily | Multi-modal: text, images, video, structured data |
| **Customization** | Configure pre-built generators | Engineer solutions for your exact requirements |
| **Industry fit** | Generic templates | Domain-specific intelligence built in |
| **Support model** | Self-service (you figure it out) | True partnership - we take full ownership |
| **Pricing** | Subscription per row/GB | Project-based - you own the solution |
| **Edge cases** | Works for common scenarios | Excels at complex, novel requirements |
The right choice depends on your requirements. If a platform fits your use case, use it. If it doesn't, that's where we come in.
## Conclusion and Next Steps
Synthetic data generation provides a privacy-preserving solution for modern development challenges, enabling teams to build and test AI systems without exposing sensitive production data. The technology bridges the gap between data utility requirements and regulatory compliance, while addressing fundamental problems of data scarcity and acquisition costs.
**Immediate actionable steps:**
* Assess your current data constraints: identify where access restrictions or scarcity limit development velocity or model performance
* Pilot with a bounded use case: start with test data generation for a single service to build organisational familiarity
* Evaluate tools against your requirements: match your data types and technical needs against available frameworks and platforms
* Consider whether your requirements fall outside what platforms can handle - if so, custom engineering is worth exploring
---
### Your product deserves synthetic data engineered for it
Whether you're building the next innovative product, training specialised AI models, or solving unique data challenges, generic platforms often won't cut it. You bring the product vision. We bring the product-building expertise - battle-tested technology, true partnership, and the engineering depth to solve problems platforms can't touch.
Get in touch: [hello@rumblefish.dev](mailto:hello@rumblefish.dev) | [Read about Synthetic Data Generation services](https://www.rumblefish.dev/services/synthetic-data-generation/)
Synthetic Data Generation: A Complete Guide for 2026If you're building AI models, running software tests, or navigating the maze of data privacy compliance, you've probably run into the same wall: the data you need is either locked away, too expensive to collect, or legally off-limits. Synthetic data generation is how the smartest teams are breaking through that wall - and in this guide, we'll show you exactly how it works.
Synthetic data generation is the process of creating artificial datasets that replicate the statistical properties, patterns, and correlations of real-world data without incorporating any actual individual records or sensitive information. This technology has become essential for organisations navigating the intersection of data-driven innovation and privacy compliance. At Rumble Fish, we've seen this challenge play out across DeFi protocols, fintech platforms, and AI-powered products. Whether you're simulating on-chain transaction behaviour, generating training data for ML models, or stress-testing a financial system, synthetic data is no longer a workaround - it's a battle-tested strategy.
---
**TL;DR**
Synthetic data generation uses algorithms, statistical models, and AI techniques to create artificial data that preserves the statistical properties of real data while eliminating privacy risks. The generation process analyses original data patterns and recreates them as entirely new data points that contain no traceable personal information.
---
After reading this guide, you will understand:
* How synthetic data generation processes work at a technical level
* The different types of synthetic data and their specific applications
* Which tools and frameworks fit your use case
* How to address data quality, scalability, and compliance challenges
* Practical steps to implement synthetic data in your development workflow
* Why custom engineering often beats off-the-shelf platforms - and when to use each
## Understanding Synthetic Data Generation
Synthetic data generation refers to **creating artificial data that maintains the utility and statistical characteristics of existing data** without exposing sensitive production data. This artificially generated data serves as a privacy-preserving alternative for AI training, test data generation, analytics, and simulations across industries. For modern software development teams, the ability to generate synthetic data solves several critical problems: data scarcity in underrepresented scenarios, privacy restrictions on production data access, and the high costs of acquiring and labelling real data. Data scientists can train robust machine learning models, run load and performance tests, and develop new features without ever touching actual sensitive information.
### Types of Synthetic Data
**Structured synthetic data** includes tabular data, relational database records, and financial transaction logs. This type is particularly valuable for fintech applications where generating realistic tabular data enables fraud detection model training and payment system testing without exposing real customer data to risk.
**Unstructured data** encompasses images, text, audio, and video generated through deep learning models. Natural language processing applications benefit from synthetic text that mimics real communication patterns, while computer vision systems train on generated images representing scenarios difficult to capture in production.
**Time-series synthetic data** covers sensor readings, transaction logs, market data, and sequential events. For blockchain and DeFi applications, this includes simulated on-chain activity, protocol interactions, and smart contract transaction patterns that would be impossible to collect at scale from live networks.
Each type connects to specific development needs: structured formats support database testing and analytics, unstructured formats enable AI model training, and time-series data powers simulation and performance testing.
### Synthetic vs. Real vs. Anonymised Data
Traditional anonymisation techniques - data masking, tokenisation, generalisation - modify real data to obscure identities. However, these approaches carry re-identification risks when combined with external datasets, and often degrade data utility by removing the contextual information essential for analysis. Synthetic data fundamentally differs because **it contains no actual data from real individuals**. The generator creates data that is statistically identical to the source but shares zero one-to-one correspondence with original records. This distinction matters significantly for regulatory compliance: while anonymised data may still fall under GDPR or HIPAA scope if re-identification is possible, properly generated synthetic data typically does not. The utility preservation advantage is equally important. Anonymisation often destroys the correlations and statistical relationships needed for meaningful analysis. **Synthetic data maintains these patterns - mean, variance, multivariate dependencies - while eliminating privacy risks entirely.**
## How Synthetic Data Generation Works
The synthetic data generation workflow follows a consistent arc: analyse source data to extract patterns, build models that capture those patterns, and generate new data points that embody the learned characteristics without reproducing original records. The sophistication of each step determines the quality and utility of the resulting synthetic datasets.
### Statistical Distribution Modelling
Statistical approaches form the foundation of many synthetic data generation pipelines. The process begins with analysing the probability distributions present in the original data - identifying whether variables follow Gaussian, uniform, exponential, or custom distributions, and estimating their parameters.
Copula models extend this by capturing multivariate dependencies between variables. Rather than assuming independence or simple correlations, copulas model the joint distribution structure, enabling the generation of data samples that honour complex relationships between columns in tabular data - critical when, for example, a synthetic financial transaction needs to respect correlations between amount, merchant category, and time of day. These methods excel when interpretability matters and when data relationships are well-understood. Implementation complexity varies: univariate distribution matching is straightforward, while accurately modelling high-dimensional dependencies requires careful statistical validation.
### Machine Learning-Based Generation
Machine learning models learn patterns from training data through supervised and unsupervised approaches. Neural networks, particularly deep learning models, capture non-linear relationships and complex feature interactions that statistical methods can miss. Supervised approaches train on labelled datasets to generate synthetic data with known properties. Unsupervised methods discover latent structure in unlabelled data, enabling the generation of realistic data that reflects inherent patterns without explicit specification. **The relationship between ML and statistical methods is complementary:** statistical techniques provide interpretable baselines and work well for structured formats, while ML approaches handle the complexity of unstructured data and high-dimensional feature spaces where explicit modelling becomes intractable.
### Simulation-Based Approaches
Monte Carlo methods generate data through repeated random sampling based on defined probability models. Agent-based modelling creates synthetic datasets by simulating individual actors following behavioural rules, producing emergent patterns that mirror real system dynamics. Physics-informed simulations and 3D environment rendering generate annotated datasets for autonomous systems, robotics, and computer vision. These approaches produce perfectly labelled training data for scenarios that would be dangerous, expensive, or impossible to capture from real environments. For blockchain applications, simulation-based approaches can model network behaviour, transaction propagation, and smart contract execution. DeFi protocol testing benefits from simulated market conditions, liquidation cascades, and multi-step transaction sequences that stress-test behaviour under extreme scenarios.
These three technical foundations - statistical, ML-based, and simulation-driven - often combine in production systems, with the choice depending on data type, fidelity requirements, and computational constraints.
## Synthetic Data Generation Techniques and Implementation
Practical implementation requires selecting appropriate generative models and integrating them into development workflows. Here's what development teams need to know when moving from theory to production.
### Generative AI Models
**Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)** pit two neural networks against each other: a generator that creates synthetic samples and a discriminator that learns to distinguish generated data from real data. This adversarial dynamic iteratively refines output until the synthetic data becomes statistically indistinguishable from the original. GANs are powerful but can suffer from training instability and mode collapse, where the generator learns to produce only a narrow range of outputs.
**Variational Autoencoders (VAEs)** encode data into a compressed latent space and learn probabilistic mappings that enable sampling of new data points. VAEs offer more stable training than GANs and provide smooth interpolation between data samples, making them well-suited to applications where diversity and controllability matter.
**Transformer-based models** - including large language models like GPT-4o - are increasingly applied to tabular and structured data generation by treating rows or records as sequences and learning dependencies across columns. These models excel at capturing long-range relationships and can be prompted with chain-of-thought reasoning to produce contextually accurate, culturally authentic outputs - a technique we used to great effect in the Panenka AI project (more on that below).
General implementation workflow:
1. **Train the base model** on the original dataset with appropriate preprocessing and validation splits
2. **Configure generation parameters** and constraints (privacy budgets, value ranges, referential integrity rules)
3. **Generate synthetic samples** in batches, monitoring for mode collapse or distribution drift
4. **Validate output quality** through statistical fidelity metrics and downstream task performance
5. **Deploy the synthetic dataset** with appropriate documentation and lineage tracking
### Framework Comparison
| **Framework** | **Best For** | **Complexity** | **Notes** |
| --- | --- | --- | --- |
| TensorFlow / Keras | Custom GAN/VAE architectures, deep learning | High | Custom implementation required |
| Scikit-learn | Statistical methods, rapid prototyping | Medium | Standard tabular formats |
| Synthetic Data Vault (SDV) | Relational databases, tabular data | Low | Good for financial data structures |
| CTGAN | Mixed data types, complex distributions | Medium | Effective for transaction patterns |
Selecting the right tools depends on data complexity, team ML expertise, and pipeline integration requirements. For teams new to synthetic data, the Synthetic Data Vault offers accessible APIs. Teams with established ML infrastructure may prefer CTGAN or custom GAN implementations for greater control. For novel multi-modal requirements - like generating images, names, and behavioural patterns together - custom engineering is typically the only viable path.
## Real-World Example: Panenka AI - Gaming Synthetic Data at Scale
Panenka, an AI-powered football manager game, needed to generate 20,000+ unique player profiles - each with culturally diverse and realistic names from different countries, photorealistic faces with distinct features, and consistent ageing progression throughout a player's career, all without copyright violations or privacy concerns.
This is exactly where off-the-shelf synthetic data platforms hit their limits:
* Generic name generators produced repetitive, culturally inauthentic names and collided with famous footballers
* Basic image generation tools produced inconsistent outputs with no ageing capability
* Standard synthetic data platforms are built for structured tabular data, not multi-modal gaming assets
Our custom solution combined GPT-4o with Chain of Thought prompting and Self Consistency to generate culturally relevant names based on nationality - accounting for each country's diversity and cultural nuance while avoiding famous name combinations. For faces, we developed a 'genetic' approach: building detailed lists of facial element descriptors (lips, noses, eyebrows, cheekbones, freckles), then used GPT-4o to translate these into structured prompts that Leonardo.ai could process effectively. Player ageing was achieved by storing the original generation parameters (prompt, seed, and settings), ensuring appearance consistency as players progressed through their careers.
**The result:** a fully scalable, privacy-safe synthetic data pipeline purpose-built for an entertainment product that no existing platform could have delivered. [Read the full case study here.](https://www.rumblefish.dev/case-studies/panenka/)
## Common Challenges and Solutions
Implementing synthetic data generation in production environments surfaces practical obstacles that development teams must address systematically.
### Data Quality and Fidelity
Generated data quality depends on how well synthetic datasets preserve the statistical properties of real data while maintaining utility for downstream tasks. Implement validation using multiple metrics: Kolmogorov-Smirnov tests for distribution matching, correlation matrix comparisons for relationship preservation, and downstream task performance parity.
High-quality data generation requires domain expert review alongside automated validation. A/B testing between synthetic and real data in non-critical applications can reveal subtle fidelity gaps that statistical tests alone may miss. Treat synthetic data quality as an ongoing process, not a one-time checkpoint.
### Scalability and Performance
Generating realistic synthetic data at enterprise scale, billions of records with complex interdependencies, strains computational resources. Optimise generation pipelines through distributed computing frameworks that parallelise independent generation tasks. Implement incremental generation strategies that produce data on demand rather than pre-generating massive datasets. Cloud infrastructure with auto-scaling (AWS is our stack of choice) enables burst capacity for load and performance testing scenarios that require high volumes.
### Regulatory Compliance and Privacy
While synthetic data eliminates direct privacy risks, regulators increasingly scrutinise generation processes. Establish differential privacy methods that provide mathematical guarantees on information leakage. Document generation methodology, training data sources, and validation results to demonstrate compliance.
For GDPR, CCPA, and industry-specific regulations, maintain audit trails showing that no sensitive data persists in synthetic outputs. For high-stakes applications in healthcare or finance, consider third-party validation of your generation processes. Properly implemented synthetic data is one of the most robust privacy-preserving strategies available - but "properly implemented" is doing a lot of work in that sentence.
### Custom Engineering vs. Off-the-Shelf Platforms
This is a question we get often. Platforms like Gretel, MOSTLY AI, and Tonic are excellent for common use cases involving structured tabular data. They're quick to set up and require no ML expertise. But they have hard limits.
When your requirements are complex, multi-modal, or domain-specific, **custom engineering pays for itself.** Here's how the two approaches compare:
| | **Synthetic Data Platforms** | **Rumble Fish Custom Engineering** |
| --- | --- | --- |
| **Data scope** | Structured/tabular data primarily | Multi-modal: text, images, video, structured data |
| **Customization** | Configure pre-built generators | Engineer solutions for your exact requirements |
| **Industry fit** | Generic templates | Domain-specific intelligence built in |
| **Support model** | Self-service (you figure it out) | True partnership - we take full ownership |
| **Pricing** | Subscription per row/GB | Project-based - you own the solution |
| **Edge cases** | Works for common scenarios | Excels at complex, novel requirements |
The right choice depends on your requirements. If a platform fits your use case, use it. If it doesn't, that's where we come in.
## Conclusion and Next Steps
Synthetic data generation provides a privacy-preserving solution for modern development challenges, enabling teams to build and test AI systems without exposing sensitive production data. The technology bridges the gap between data utility requirements and regulatory compliance, while addressing fundamental problems of data scarcity and acquisition costs.
**Immediate actionable steps:**
* Assess your current data constraints: identify where access restrictions or scarcity limit development velocity or model performance
* Pilot with a bounded use case: start with test data generation for a single service to build organisational familiarity
* Evaluate tools against your requirements: match your data types and technical needs against available frameworks and platforms
* Consider whether your requirements fall outside what platforms can handle - if so, custom engineering is worth exploring
---
### Your product deserves synthetic data engineered for it
Whether you're building the next innovative product, training specialised AI models, or solving unique data challenges, generic platforms often won't cut it. You bring the product vision. We bring the product-building expertise - battle-tested technology, true partnership, and the engineering depth to solve problems platforms can't touch.
Get in touch: [hello@rumblefish.dev](mailto:hello@rumblefish.dev) | [Read about Synthetic Data Generation services](https://www.rumblefish.dev/services/synthetic-data-generation/)AI
 Running Claude as a Backend Service: How We Build AI-Powered Web Applications on AWS
Running Claude as a Backend Service: How We Build AI-Powered Web Applications on AWS By Marek Kowalski
By Marek KowalskiAI
Have an idea?
Let’s work
together!We will answer any questions you may have related to your startup journey!Do you prefer e-mail?
hello@rumblefish.pl
together!We will answer any questions you may have related to your startup journey!Do you prefer e-mail?
hello@rumblefish.pl


RUMBLEFISH POLAND SP Z O.O.Filipa Eisenberga 11/3 31-523 Kraków, Polska
NIP: 6772425725REGON: 368368380KRS: 0000696628
P: +48 601 265 364E: hello@rumblefish.dev
Copyright © 2026 RumblefishServicesBlockchain Software DevelopmentZero-Knowledge Proof DevelopmentXRPL Blockchain DevelopmentSmart Contract DevelopmentDeFi DevelopmentAWS Cloud SolutionsAI Chat Assistant DevelopmentSynthetic Data GenerationFintech Software DevelopmentDedicated Development TeamsWeb developmentMobile developmentIT Services for startupUI/UXRust Web App DevelopmentView all services
CareersJoin Our Team



