
Building on XRP Ledger: All the Basics You Must Know
Mon, Aug 11, 2025 •10 min read
Unlike bitcoin and traditional blockchain systems that rely on energy-intensive mining, XRP Ledger offers developers a fundamentally different approach to building financial applications. This open-source Layer-1 blockchain technology was a digital asset designed specifically for fast, low-cost payments and includes native features like a decentralized exchange, escrow, and payment channels that eliminate the need for complex smart contracts.
With settlement times of just 3-5 seconds and transaction costs averaging 0.00001 XRP, XRPL has become an attractive platform for financial institutions and developers looking to build scalable payment solutions. The network processes transactions per second efficiently while maintaining security through its unique consensus process, making it a compelling alternative for projects built on solving real-world payment challenges. This comprehensive guide covers all the basics you must know about building on the XRP Ledger, from understanding its architecture to implementing your first application. Whether you’re exploring alternatives to traditional banking systems or looking to leverage digital currencies for cross-border transactions, you’ll discover why XRPL’s design makes it a top priority for modern fintech development.
Understanding XRP Ledger Architecture
XRP Ledger operates as a Layer-1 blockchain using the XRP Ledger Consensus Protocol (XRPLCP) instead of Proof of Work mining like Bitcoin. This consensus process relies on trusted validators who maintain unique node lists (UNL), essentially a curated set of validators each node trusts for reaching agreement on transaction sets. The network achieves consensus when at least 80% of a validator’s UNL agrees on the next set of transactions to execute them. This typically occurs every 3-5 seconds, providing near-instant finality that surpasses traditional banking systems and most other blockchain networks.
Ledger Structure and State Management
A ledger on XRPL functions as a validated block containing state data, transaction sets, and metadata. The state is organized as a Merkle-tree-like structure with 256-bit IDs, storing objects such as:
- AccountRoot entries for user accounts
- RippleState for trust lines between accounts
- Offer objects for DEX orders
- Escrow and PayChannel objects for conditional payments
This architecture enables efficient state verification and consistent hashing across all network participants, ensuring every validator maintains an identical view of the ledger.
XRP Tokenomics
All 100 billion XRP tokens were pre-created at genesis, with a significant portion initially distributed to Ripple Labs Inc. This pre-mined approach eliminates the energy consumption associated with mining while introducing a deflationary mechanism through transaction fee burning. Every transaction on the network requires a small fee in XRP drops (1 XRP = 1,000,000 drops) that gets permanently destroyed, creating deflationary pressure tied to network usage. This fee structure serves dual purposes: preventing spam from bad actors and gradually reducing the total XRP supply over time.
Core Development Concepts
Building on the XRP Ledger requires understanding several fundamental concepts that differ significantly from other blockchain platforms. These basics form the foundation for all development work on the network.
Account Management and Reserves
Every account on XRPL must maintain a base reserve of XRP to prevent spam and maintain ledger integrity. Currently set at 10 XRP, this reserve ensures that creating a new account has economic friction while keeping the barrier reasonable for legitimate users.
Beyond the base reserve, accounts require additional “owner reserves” for each ledger object they create, such as:
- Trust lines for holding digital currencies
- Open orders on the decentralized exchange
- Escrow agreements
- Payment channels
When these objects are deleted, the associated reserve funds become available again, providing flexibility in account management.
Transaction Types and Execution
XRPL supports several native transaction types that handle different aspects of value transfer and asset management:
Payment Transactions: Send XRP or issued currencies between accounts, with support for multi-currency paths and automatic currency conversion.
OfferCreate/OfferCancel: Manage orders on the built-in decentralized exchange for trading digital assets without intermediary currency requirements.
EscrowCreate/EscrowFinish: Lock funds under time-based or cryptographic conditions, enabling conditional payments that settle automatically when criteria are met.
CheckCreate/CheckCash: Issue deferred payments that recipients can claim when ready, similar to traditional checks but with cryptographic security.
Each transaction type serves specific use cases while maintaining the low cost and fast settlement that characterizes the XRP ecosystem.
Trust Lines and Issued Currencies
Trust lines represent bilateral credit relationships between accounts, enabling the creation and management of digital currencies beyond native XRP. These relationships form the basis for tokenization on XRPL, supporting everything from fiat-backed stablecoins to utility tokens.
Issuers can configure various parameters for their digital currencies:
- Transfer fees for each transaction
- Freeze capabilities for regulatory compliance
- Global freeze options for emergencies
- Default rippling settings for liquidity optimization
This flexibility makes XRPL suitable for regulated environments where financial institutions need granular control over digital asset behavior.
Built-in Features for DeFi Development
One of XRPL’s most compelling aspects for developers is its comprehensive suite of native DeFi features that function without requiring external smart contracts. These built-in capabilities reduce complexity while maintaining the security and efficiency that make the XRP Ledger attractive for financial applications.
Decentralized Exchange and Auto-Bridging
XRPL includes a native decentralized exchange where users can trade XRP and issued currencies through order books integrated directly into the consensus mechanism. This eliminates the need for external DEX protocols while ensuring atomic settlement of trades.
The auto bridging feature uses XRP as an intermediary currency to connect fragmented liquidity across trading pairs. When direct markets lack sufficient depth, the system automatically routes through XRP order books to find better composite prices, effectively making XRP a bridge currency for all trading activity.
Payment Channels for Micropayments
Payment channels enable high-throughput, off-ledger micropayments between parties while maintaining on-ledger security guarantees. Once established, channels allow unlimited small amounts to be transferred with minimal on-chain interaction, making them ideal for:
- Content monetization and streaming payments
- IoT device transactions
- Gaming and digital services
- Machine-to-machine value transfer
Channels provide the scalability needed for applications requiring frequent, small-value transfers without overwhelming the main network.
Escrow for Conditional Payments
Native escrow functionality enables time-locked or condition-based payments without complex smart contract development. Developers can create escrows that:
- Release funds automatically after a specific time
- Require cryptographic proof before releasing funds
- Enable atomic swaps between different assets
- Support milestone-based payments for services
This built-in escrow system has proven particularly valuable for cross-border transactions where parties need assurance of payment completion.
Feature
Traditional Banking
Bitcoin
Ethereum
XRP Ledger
Settlement Time
1-5 days
10-60 minutes
1-15 minutes
3-5 seconds
Transaction Cost
$15-50
$1-50
$1-100+
$0.00001
Energy Usage
High
Very High
High
Minimal
Built-in DEX
No
No
External
Native
Regulatory Features
Limited
No
Limited
Extensive
Development Tools and APIs
XRP Ledger provides a comprehensive development infrastructure that makes building applications straightforward and efficient. The ecosystem includes robust APIs, multiple programming language libraries, and extensive documentation to support developers at all experience levels.
Core Infrastructure
The rippled server forms the backbone of XRPL development, serving as both the peer-to-peer consensus participant and the API gateway for applications. Developers can either run their own rippled instance or connect to public endpoints for development and production use.
The server exposes two primary API interfaces:
- JSON-RPC: Traditional request-response API for querying ledger state and submitting transactions
- WebSocket: Real-time streaming interface for monitoring ledger changes and transaction status
Both interfaces provide comprehensive access to account information, order books, pathfinding services, and transaction history.
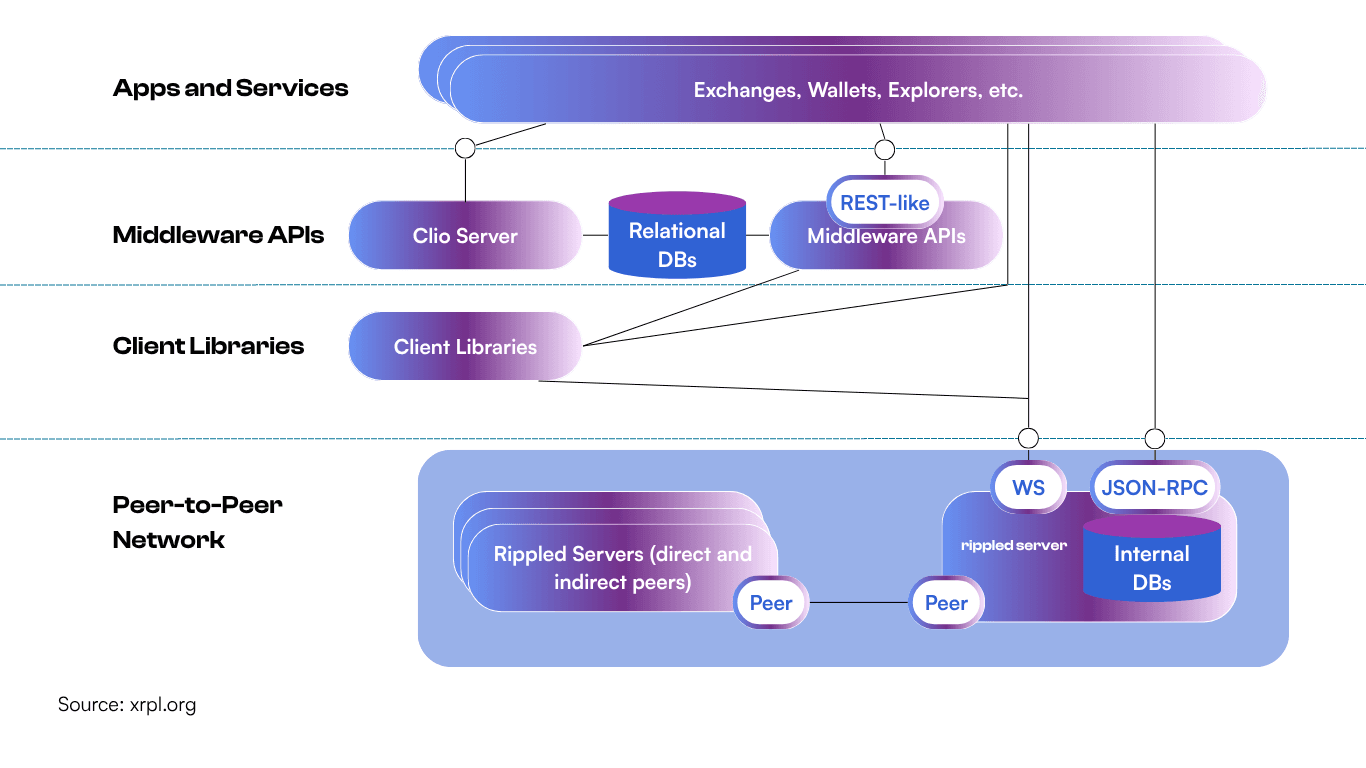
Official Libraries and SDKs
XRPL maintains official libraries in multiple programming languages:
- JavaScript/TypeScript (xrpl.js): Full-featured library with browser and Node.js support
- Python (xrpl-py): Comprehensive Python integration for backend services
- Java: Enterprise-ready library for JVM-based applications
These libraries abstract away the complexity of transaction construction, cryptographic signing, and network communication while providing high-level interfaces for common operations.
Testing and Development Environment
The XRPL testnet provides a complete mirror of mainnet functionality with free test XRP available through faucets. This environment enables developers to:
- Test transaction flows without risking real funds
- Experiment with advanced features like escrow and payment channels
- Validate integration patterns before mainnet deployment
- Benchmark application performance under realistic conditions
Professional development teams like Rumble Fish Software Development leverage these tools to build production-ready applications that integrate XRPL’s native features with enterprise-grade security and compliance requirements.
Popular dApps and Use Cases
The XRPL ecosystem has evolved to include diverse applications that demonstrate the practical value of building on this blockchain technology. These projects built on XRPL showcase how developers can leverage native features to create innovative financial services.
Leading DeFi Applications
XPMarket serves as the largest XRPL dApp, offering integrated DEX trading, AMM functionality, lending pools, and NFT marketplace services. The platform demonstrates how to combine multiple XRPL features into a comprehensive DeFi experience.
xrp.cafe operates as the leading NFT marketplace for XRPL-native digital collectibles, showcasing the network’s built-in NFT capabilities without requiring external smart contract deployments.
Educational and Development Tools
DeFi-Island provides a 3D open-source virtual environment on XRPL testnet where users can interactively learn about blockchain concepts, DEX trading, and payment flows. This project demonstrates XRPL’s accessibility for educational applications.
Various analytics dashboards and developer tools help teams monitor network activity, track token performance, and analyze trading patterns across the decentralized exchange.
Enterprise and Payment Solutions
XRPL’s design makes it particularly well-suited for enterprise payment applications. Financial institutions use the network to settle cross-border transactions more efficiently than traditional banking systems, often leveraging XRP as a bridge currency to reduce liquidity requirements.
Payment service providers integrate XRPL to offer customers faster international transactions with greater transparency and lower costs than conventional correspondent banking networks.
Real-World Applications
XRP Ledger’s practical applications extend far beyond typical cryptocurrency use cases, addressing real-world problems in payments, finance, and digital asset management. These applications demonstrate why building on the XRP Ledger offers unique advantages for solving business challenges.
Cross-Border Payments and Remittances
Traditional international transactions often require multiple intermediary banks, creating delays and high fees. XRPL enables direct settlement between parties or through liquidity pools, dramatically reducing both time and cost. Financial institutions can use XRP as a bridge currency to settle cross-border transactions without maintaining pre-funded Nostro/Vostro accounts in multiple currencies. This approach reduces capital requirements while improving liquidity management across different fiat currencies. The network’s pathfinding capability automatically discovers the most efficient route for multi-currency transactions, whether through direct exchange or via intermediate assets, ensuring optimal execution for each payment.
Micropayments and Content Monetization
Payment channels enable new business models based on micropayments that would be economically impossible on other networks. Content creators can monetize their work through pay-per-view models, while service providers can charge for API calls or bandwidth usage with minimal overhead.
These capabilities support emerging use cases like:
- Real-time content streaming with per-second payments
- IoT device transactions for machine-to-machine services
- Gaming applications with micro-rewards and in-game purchases
- Educational platforms with granular access control
Tokenization and Asset Management
XRPL’s issued currency system enables comprehensive tokenization of real-world assets, from traditional fiat-backed stablecoins to more complex financial instruments. Issuers can implement sophisticated compliance controls, including:
- Selective freezing capabilities for regulatory compliance
- Transfer fees to fund operations or provide yield
- Multi-signature controls for institutional governance
- Automatic compliance checks through account flags
Recent developments include the launch of regulated USD stablecoins that provide institutional-grade settlement infrastructure with full regulatory oversight.
Liquidity Provision and Market Making
The native DEX enables sophisticated liquidity provision strategies without requiring external protocols. Market makers can provide depth across multiple currency pairs while benefiting from auto-bridging to improve capital efficiency. Unlike traditional market making, XRPL’s order books settle atomically as part of the consensus process, eliminating many risks associated with external smart contract interactions while providing deterministic execution guarantees.
Getting Started with Development
Beginning your journey building on the XRP Ledger requires understanding the development workflow and establishing the proper tools and environment. The process differs significantly from other blockchain platforms, but XRPL’s comprehensive documentation and tooling make onboarding straightforward.
Setting Up Your Development Environment
Start by choosing your development approach: you can either run a local rippled server for complete control or connect to public testnet endpoints for faster initial development. Most developers begin with public endpoints to avoid infrastructure complexity.
Install the appropriate XRPL library for your preferred programming language. The JavaScript library (xrpl.js) provides the most comprehensive feature set and active community support, making it ideal for both frontend and backend development.
Create testnet accounts using the official faucet and experiment with basic operations like sending payments, creating trust lines, and placing orders on the DEX. This hands-on experience helps developers understand XRPL’s unique transaction model and fee structure.
Essential Development Patterns
Unlike platforms that rely heavily on smart contracts, XRPL development focuses on combining native features to achieve complex functionality. Key patterns include:
State Management: Understanding how accounts, reserves, and object ownership affect application design and user experience.
Transaction Sequencing: Managing sequence numbers and handling potential transaction failures or network delays.
Multi-Currency Operations: Leveraging pathfinding and auto-bridging for optimal currency conversion and settlement.
Conditional Logic: Using escrow, checks, and multi-signature features to implement business logic without external contracts.
Best Practices for Production Applications
Implement comprehensive error handling that accounts for XRPL’s specific response codes (tec, tem, ter) and transaction lifecycle. Always wait for ledger validation before considering transactions final, and design retry logic for network connectivity issues.
Practice secure key management by signing transactions client-side or in hardware security modules. Never transmit private keys or store them in application code. Consider multi-signature setups for high-value operations to distribute security risks.
Test extensively on testnet, particularly focusing on edge cases around reserves, object lifecycles, and fee dynamics under varying network loads. Validate that your application handles partial fills on DEX orders and other non-deterministic outcomes gracefully.
Professional development teams like Rumble Fish Software Development can accelerate this process by providing expertise in XRPL architecture, security best practices, and integration with compliance requirements that financial institutions demand.
Security Considerations
Security on XRP Ledger requires understanding both the network’s built-in protections and implementing appropriate application-level safeguards. While XRPL’s consensus mechanism provides strong network security, developers must address key management, transaction signing, and operational security concerns.
Key Management and Cryptographic Security
XRPL uses elliptic curve cryptography for account creation and transaction signing. Private keys must be generated using cryptographically secure random number generators and protected throughout their lifecycle. Implement multi-signature configurations for high-value operations, allowing you to distribute trust across multiple keys and geographic locations. XRPL’s native multi-sign feature supports sophisticated M-of-N schemes without requiring external smart contracts. Consider separating master keys from regular keys, using the master key only for account configuration changes while conducting daily operations with regular keys that can be rotated if compromised.
Operational Security Measures
Enable two-factor authentication on all accounts that have access to operational infrastructure, including API endpoints, development environments, and any custodial services used for treasury management. Monitor account activity using XRPL’s subscription capabilities to detect unauthorized transactions or suspicious patterns. Implement automated alerts for significant balance changes, new trust line creation, or unexpected trading activity. Protect rippled endpoints with appropriate rate limiting and ensure all communications use TLS encryption. If running your own validator, follow security hardening practices, including network segmentation and regular security updates.
Application-Level Risk Management
Design applications to handle various failure modes gracefully, including network partitions, temporary validator outages, and potential consensus delays. Implement circuit breakers and fallback mechanisms for critical operations. Validate all user inputs and implement appropriate sanity checks for transaction amounts, destination addresses, and fee calculations. Consider implementing spending limits and approval workflows for large transactions. Regularly review account configurations, trust line settings, and issuer controls to ensure they align with current business requirements and regulatory obligations. Monitor for potential security vulnerabilities in any third-party integrations or bridge protocols.
Future Development Opportunities
The XRPL ecosystem continues evolving with new features, integrations, and use cases that expand the possibilities for developers building on the platform. Understanding these trends helps inform strategic development decisions and identify emerging opportunities.
Institutional Adoption and Compliance
The launch of regulated stablecoins like RLUSD in late 2024 has opened new opportunities for institutional applications. These assets provide the stability and regulatory clarity that traditional financial institutions require while leveraging XRPL’s speed and cost advantages. Financial institutions increasingly explore XRPL for treasury operations, correspondent banking replacement, and settlement optimization. The New York State Department of Financial Services and other regulators have provided clearer guidance on digital asset usage, creating a more predictable environment for enterprise adoption.
DeFi Ecosystem Expansion
Beyond basic payments, XRPL’s DeFi ecosystem is expanding into lending, derivatives, and yield generation strategies. Developers can build sophisticated financial products by combining native features like the DEX, escrow, and payment channels with off-ledger computation and oracle integration. Liquidity pools and automated market-making strategies benefit from XRPL’s deterministic execution and low fees, enabling new approaches to capital efficiency and risk management that weren’t economically viable on higher-cost networks.
Cross-Chain Interoperability
Bridge protocols and cross-chain infrastructure enable asset movement between XRPL and other blockchain networks, expanding the addressable market for XRPL-based applications. However, developers must carefully evaluate the security implications of any cross-chain integration. Native XRPL features often provide better security guarantees than bridged alternatives, so teams should prioritize XRPL-native solutions where possible while using bridges judiciously for specific interoperability requirements.
Emerging Use Cases
The combination of fast settlement, low costs, and built-in compliance features positions XRPL well for emerging applications in:
- Central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) and government payment systems
- Supply chain finance and trade settlement
- Carbon credit trading and environmental asset tokenization
- High-frequency trading and algorithmic market making
These applications leverage XRPL’s unique combination of performance, regulatory alignment, and native DeFi features to solve problems that other blockchain platforms struggle to address effectively.
Conclusion
Building on XRP Ledger offers developers a unique opportunity to create financial applications that combine the benefits of blockchain technology with the performance and compliance features that real-world businesses require. Unlike systems that rely on energy-intensive mining or complex smart contract deployments, XRPL provides native features for payments, trading, and asset management that work efficiently out of the box. The platform’s 3-5 second settlement times, minimal transaction costs, and built-in DeFi capabilities make it particularly well-suited for applications that need to compete with traditional banking systems on speed and cost while providing the transparency and programmability that digital assets enable.
As the ecosystem continues growing with institutional adoption, regulatory clarity, and expanding DeFi applications, developers who master XRPL’s unique architecture and native features will be well-positioned to build the next generation of financial technology solutions. Whether you’re exploring cross-border payment solutions, building DeFi applications, or tokenizing real-world assets, understanding these basics provides the foundation for successful XRPL development. For teams ready to build production applications, partnering with experienced developers like Rumble Fish Software Development can accelerate implementation while ensuring security, compliance, and scalability requirements are met from day one.
The future of finance increasingly demands the combination of speed, cost-efficiency, and regulatory alignment that XRP Ledger provides. By mastering these fundamentals, developers can participate in building the infrastructure that will power tomorrow’s global financial system.
Recent posts








